# Database
Database in itself is data-structure problem at scale. How do we organize, collect, store data in a way such that we can use relationships / associations to query targeted data.
- DBMS - Database management system
- is the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the Database itself to capture and analyze the data.
- Database Model
- How data is stored, organized and manipulated internally by the DBMS.
- Hierarchical Database
- Object Model - JavaScript in browser v8 engine
- Document Model - page data on browser when a URL response is rendered
- Relations Database Models - SQL and MySQL
- Non-Relational Databases aka noSQL - MongoDB, Firebase
# SQL based Terminologies
todo add examples to each :exclaimation:
- DCL - Data control language
- controls access to data;
- DDL - Data definition language
- defines data types such as creating, altering, or dropping tables and the relationships among them;
- DML - Data manipulation language
- performs tasks such as inserting, updating, or deleting data occurrences;
- DQL - Data query language
- allows searching for information and computing derived information.
- Relationships
- are a logical connection between different tables, established on the basis of interaction among these tables.
- Transactions
- ACID Transactions to support rollback in case of failures. ACID Transactions to build reliable and secure business critical applications.
- SP - Stored procedures
- restrict access to DBMS only through SP
- Associative table
- A relational database requires the implementation of a base relation (or base table) to resolve many-to-many relationships. A base relation representing this kind of entity is called, informally, an associative table.
- Database normalization
- structure DBMS to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity.
# Database Features
- Replication
- storage redundancy, to increase data availability and resilience in case of partial failure
- Security
- Transactions and concurrency
- Easy Migrations
- Easy Backup and Restores
- Database logs, Querying tools like FQL Facebook query language
- Scaling
- Sharding
- Multiple Master - Multiple Slave
- Horizontal and vertical scaling techniques
# Database Normalization
- What is Normalization? Why do we need it?
Its a way to structure RDBMS to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity.
Codd defined 1NF, 2NF, 3NF in 1970's and then later BCNF in 1974
- What are DB dependencies? What problem do they solve?
Tries to solve data optimization problem in RDBMS
Most popular one is functional dependency
- 1NF
Decompose all Multivalued and Composite attributes to atomic attribute
Eg:Consider Employee table,EMP_ID EMP_NAME PHONE_NO 1 abc 235453 👉 2 pqr ❗️ 364868, 495789 ❗️ 3 xyz 097897 Some employee can have multiple phone numbers. If so PHONE_NO attribute becomes multivalues attribute and needs to be decomposed to atomic attribute to be in 1NF.
# How do we decompose?
Remove PHONE_NO attribute from main employee table and split it into 2 seperate tables.
- EMP_ID, EMP_NAME
- EMP_ID, PHONE_NO
EMP_ID PHONE_NO 1 235453 👉 2 364868 👉 2 495789 3 097897 EMP_ID EMP_NAME 1 abc 2 pqr 3 xyz
# Functional Dependency - FD
| Attribute A | Attribute B | FD check |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | X | holds |
| 1 | X | holds |
| 2 | Z | holds |
| 3 | Y | holds |
| 2 | Z | holds |
| 1 | S | breaks, as expected |
Hence, because of last tuple entry, FD doesnt hold between attribute A and B
FD in primary attribute
If Attribute A is primary attribute, then FD would hold. Because primary key means all entities for attribute A would be unique, and since A is unique no repetition and B would be unique too.
# Database Relationships
Applicable to Relational DBMS, but concept extends to all other (no-SQL) DBMS as well.
A table relationship is established when a child table defines a Foreign Key column that references the Primary Key column of its parent table.
Every Database table relationship is, therefore, built on top of Foreign Key columns
# one-to-many Relationship (1:M)
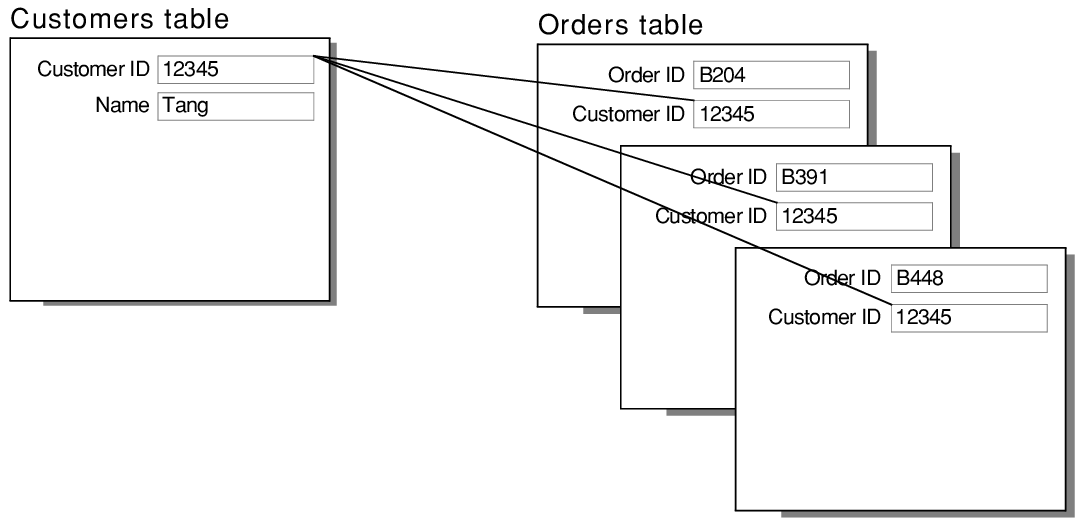
The One-to-Many relationship is defined as a relationship between two tables where a row from one table can have multiple matching rows in another table. This relationship can be created using Primary key-Foreign key relationship. It is the most common relationship.
Efficient way to join two tables with one to many relationship
# Examples,
- Customers and Orders tables.
- A book can have multiple authors.
CREATE TABLE dbo.Book (
Pk_Book_Id INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(255),
ISBN VARCHAR(255)
);
CREATE TABLE dbo.Author (
Pk_Author_Id INT PRIMARY KEY,
FullName VARCHAR(255),
MobileNo CHAR(10),
Fk_Book_Id INT FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES Book(Pk_Book_Id)
);
-- ist of all users and their permissions.
SELECT * FROM Users
JOIN UserPermissions USING (UserLogin);
# one-to-one Relationship (1:1)
requires the child table Primary Key to be associated via a Foreign Key with the parent table Primary Key column. Multiple columns in the same table have 1:1 relationship. Coule also be implemented of other tables using a Foreign Key Reference.
# Examples,
- in a marriage, each spouse has only one other spouse. This kind of relationship can be implemented in a single table and therefore does not use a foreign key.
# many-to-many Relationship (M:M)
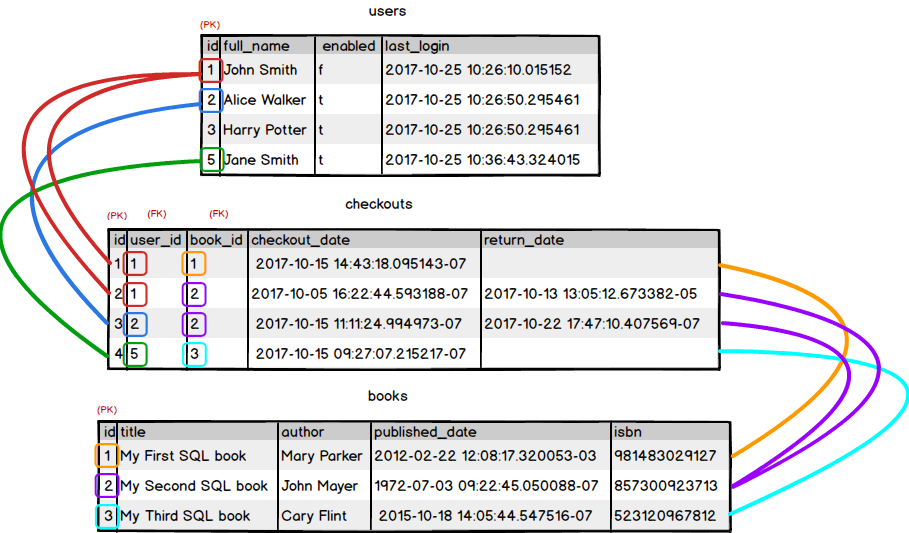
An associative entity is a term used in relational and entity–relationship theory. A relational database requires the implementation of a base relation (or base table) to resolve many-to-many relationships. A base relation representing this kind of entity is called, informally, an associative table.
It requires a link table containing two Foreign Key columns that reference the two different parent tables. Generally a many-to-many relationship is done with a junction table, like so:
CREATE TABLE employee (
employee_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
employee_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE company (
company_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
company_name VARCHAR(300) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE company_employee (
employee_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
company_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
work_hour_start TIME NOT NULL,
work_hour_end TIME NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (employee_id) REFERENCES employee (employee_id) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (company_id) REFERENCES company (company_id) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE,
PRIMARY KEY (employee_id, company_id, work_hour_start, work_hour_end)
);
SELECT e.employee_name, c.company_name, ec.work_hour_start, ec.work_hour_end
FROM employee e
INNER JOIN company_employee ec
ON e.employee_id = ec.employee_id
INNER JOIN company c
ON c.company_id = ec.company_id;
# Examples,
- relationship between the Orders and Products table. An order can contain multiple products, and a product could be linked to multiple orders: several customers might submit an order that contains some of the same products.
- Students and Courses
- Users and Permissions
# Relational DBMS
Almost 25 years old, mySQL Relational DBMS, written in C, C++, take it for a spin
docker pull mysql
# server
docker run --name some-mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw -d mysql
# client
docker exec -it some-mysql bash
# Considerations when designing a database schema
- Collect as much data as possible
- you may never know what you might need in future to scale, add new feature, analytics
- Group data logically together
- based on readability
- efficiency
- usage
# References
Most popular Database choices and why?